GP Marketing Consulting Sas, in collaboration with the Polytechnic of Milan, Plyform Composites srl and Corebon AB, developed an innovative tool based on high-modulus pitch carbon fibre, combined with the induction heating technology, to investigate the feasibility of a possible industrial application.
Pitch-based carbon fibres are particularly interesting for their mechanical and thermal properties. Thanks to the carbonization and graphitization phases, the molecular structure can reach up to 99.9% of carbon. Moreover, by virtue of the initial melt spinning - during which the precursor is pulled while being heated – the structure has a graphitic-like highly oriented composition and can exceed 900 GPa of elastic modulus. This results in an excellent thermal conductivity, up to 800 W/(m*K) (copper ≈ 400 W/(m*K)).
The materials used for this trial were supplied by Sumitomo Corporation Europe - the official European distributor of Mitsubishi DIALEAD™ pitch fibres: the balanced plain weave fabric UHM 636 P for the core and the spread-tow UHM DYF 15-150 T for the outer layer, both made with DIALEAD™ K13916 pitch-based fibre. Both fabrics were then compared with PAN-based fabrics generally used for moulds, having the same weight and impregnated with a tooling resin system (LTC) developed by Technologycom srl.
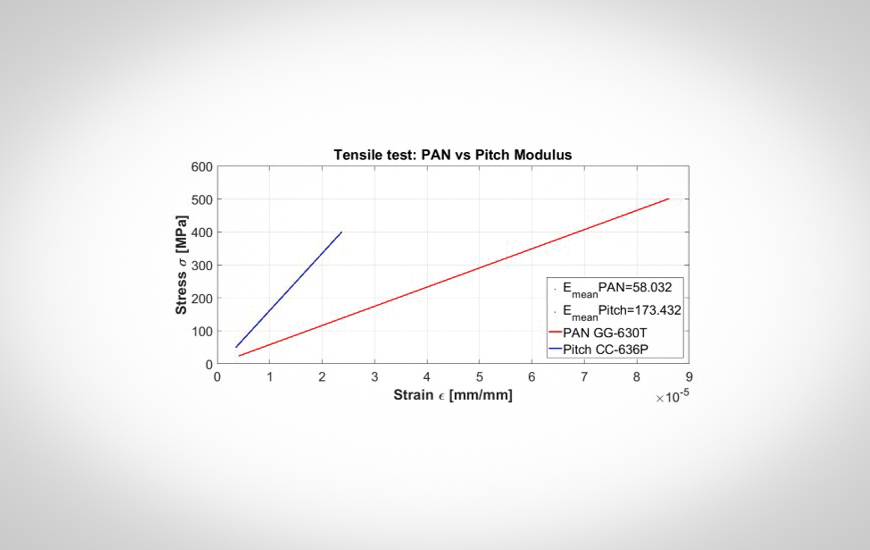
An extensive experimental campaign was then carried out to evaluate both mechanical and thermal properties of all the involved materials. The PAN-based specimens were used as reference. The results - as expected - demonstrated the higher properties of the pitch-based carbon fibre in both aspects; in particular, the elastic modulus achieved a 300% increase, compared to the PAN-based fibre.
Both moulds were laminated with a classic LTC 1-8-1 sequence, [0] for the surface and 〖"[0/+45/-45 /0]" 〗_"s" for the core. The pitch fabric showed a good drapability and an easy handling, without issues. The thermal tests in autoclave gave already very good results and the introduction of the induction heating in the next steps of the project clearly demonstrated a better thermal behaviour of the pitch tool compared with the PAN one.
Induction is a contactless method based on the physical principle of the electromagnetic induction, which consists in the direct heating of all electrically conductive materials. Thus, the heating area can be located and distributed both on the surfaces and throughout thicknesses in a totally customizable way, by using an ad hoc inductor. This allows a complete thermal volumetric control of the composite component.
In this study case, the coils were directly applied under the surface of the mould, on a backing structure. This solution enabled an even heating of the entire surface of both moulds. Looking at the thermo-camera videos, it can be easily noticed that after only 4 minutes the pitch-based tool homogeneously reached the operating set temperature, unlike the PAN-based mould, which was unable to achieve the same result.ù
To sum up, the whole work demonstrated that it is feasible to introduce and industrialize an innovative mould that can combine both mechanical and thermal advantages of the pitch-based carbon fibres with the induction heating. It results in a stiffer mould with a high efficiency level, which can be able to drastically reduce the production cycles times.
(Article by GP Marketing Consulting Sas)
-

-
16 March 2020